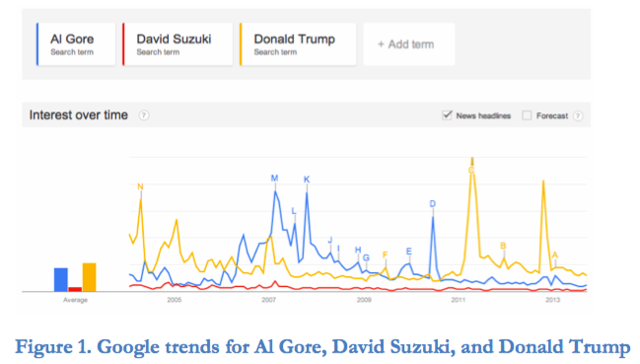
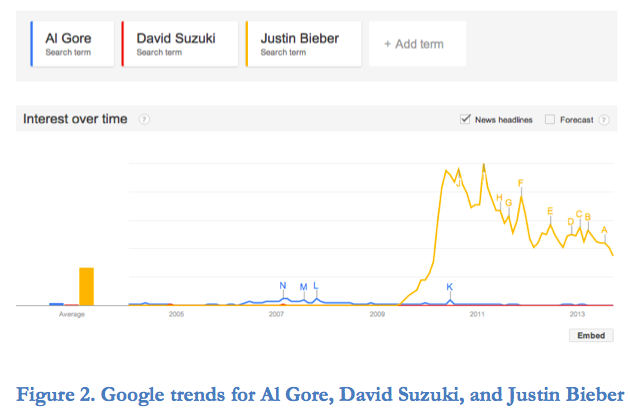
From Earth Common Journal VOL. 3 NO. 1Christopher Benjamin's Eco-Innovators: Sustainability in Atlantic Canada - Stories to Change Minds and Move HeartsSustainable Business ModelsEco-Innovators points to a number of new and more sustainable business models at opposite ends of the spectrum – the first represented here is a micro-business model proffered by Maggy Burns and the second, a green-growth model represented by Olivier Soaps. Burns, an activist and environmental worker by day, is also an entrepreneur turning other people's cast-off books into beautiful, upcycled journals – ReCover Journals – effectively saving junk from the landfill. Every season, retailers ask Burns if she has any new products for them (p. 19). While Burns did develop a few spin-off products under pressure from her distributors to stimulate demand for more stuff, ultimately she rejected this business model. "Maggy sees a strong connection between the typical growth-oriented business model and the destruction of the natural world (p. 19). It is not that she doesn't want to make money. She simply wants to do so while retaining her own ideas for sustainability. The truth is, however, that most individuals, and certainly most businesses in capitalist societies, are not yet ready to buy into this micro-business model. As Marion Copleston of the PEI Environmental Health Co-op indicates, buying less or second hand is an adjustment for most consumers, "It's a battle because we've been trained to consume," she says, "and our economy depends on consumption, our politicians are lobbied by companies that need consumption" (p. 54). Chris, himself, found this type of drive during his days at Dalhousie, saying the following: This is something I remember wrestling with in business school, this growth model that seemed just completely cancerous, because it was never questioned. In fact, there had to be annual growth. There always had to be annual positive growth in any business, without any inkling that that meant a negative impact on the ecosystem. (Interview, 2013) What if, however, there was the possibility that growth could lead to the realization of our environmental goals? Chris sees this possibility in Olivier Soaps, a Ste-Anne-deKent, New Brunswick business, creating 300,000 bars of handcrafted soap per year (p. 55). At present, Olivier Soaps sells approximately 140 products. In order to reduce packaging concerns, most of the company's bar soap is sold package-less where possible; however, Olivier is "currently working with Nova Scotia suppliers to develop biodegradable plastics" (p. 57). To date, Olivier Soaps has been so successful they have opened 14 retail shops and manufacturing facilities in Toronto, Ottawa, and La Baie, Quebec (p. 57). "They have bucked yet another trend" says Chris, "with such a decentralized operation, but Pierre says it saves shipping, fuel, and emissions to keep their factories close to their stores" (p. 59). Vice President, Pierre Pelletier, recognizes that he has bought into the growth model but sees this as the path to environmental survival. Pierre sees the need to "grow to green the supply chain" (p. 59), and Chris concurs, stating the following: The bigger they are, the more people they employ, the more people they represent, the more power they have to dictate how ingredients are grown, packaged, and shipped. Then they can impose Olivier's methods and philosophy, its respect for the environment, on others. (p. 59) In other words, if they buy into the traditional growth model with a twist, Olivier Soaps becomes a power player. They can then begin to set industry standards. Chris sees hope in these different business models. During our interview, he stated: To me, even though they're different – different world views, different business models – they all can have a positive impact ... what it boils down to is the mindset of the people running the place and if they have a strong, internalized environmental ethic, then that tends to play out in a truly green business and not a PR exercise. So, perhaps one key element in the progression of the environmental movement is the education of a new entrepreneurial elite ingrained with this ethic. This change in educational philosophy is, in fact, what is already happening around the world. Already some 514 business schools worldwide – 16 in Canada, including MacEwan University, University of Calgary, Simon Fraser University, York University, Concordia University – have signaled their agreement with this assessment by signing on as Principles for Responsible Management Education (PRME) members. The PRME are "a timely global call for business schools and universities worldwide to gradually adapt their curricula, research, teaching methodologies and institutional strategies to the new business challenges and opportunities" (PRME, 2013, para. 3) by integrating principles of corporate responsibility and sustainability. In both our interview and in Eco-Innovators, Chris outlines progress in business education options along the same lines as PRME. In our interview, for instance, he pointed to the NGO Management stream in the Masters in Environmental Studies program at York University. This program attracts "very holistically-minded, sustainability-minded people who [are] very good at organizational stuff, the very skills you learn in business school" (Interview). While his environmental concerns may have made him an outlier in Commerce at Dalhousie during his BA days, the Faculty of Management at Chris's alma mater has since established a successful sustainability program, including a Centre for Sustainability. In Eco-Innovators, Chris further identifies the Environmental and Sustainability Studies program at Acadia University, focusing on hands-on experience for students both in the community. "Given that these are real- world experiences," says Chris, "they quickly learn about roadblocks – all the barriers and excuses people throw in the way whenever we try to make change" (pp. 188-189). A community engagement course in their final year of study challenges students to come up with their own community-based initiative (p. 189), providing them with yet more experience to take into their careers after university. Re-Branding the EnvironmentEnvironmentalists have much to learn from business, particularly with regards branding and marketing. In his article "Branding the Environment" in The Coast from January 28, 2010, Chris identifies the crux of the problem for the environmental brand: In the fight for those hearts and minds, the eco-freaks are up against capitalism's finest and most financed, the captains of industrial marketing, the manufacturers of cool. Environmentalists have countered with big ideas and righteous souls---and are decidedly uncool. (para. 2) The environmentalist movement, says Chris, "tends to be seen as flaky and abstract. David Suzuki is one of our most famous members ...and he can never compare to Justin Bieber. There's just no rock star version of the environmentalist and that is ultimately a branding exercise..." (Interview, 2013). A Google trend analysis certainly supports this argument, with David Suzuki almost non-existent in both infographics below. Al Gore faired considerably better after An Inconvenient Truth was released in May of 2006, but his star seems to have waned, while that of the ultimate capitalist, Donald Trump, pulled a branding coup with The Apprentice.
As Figure 2 indicates, in the grand scheme of branding and marketing, no one is even playing the same game as Justin Bieber.
In "Branding the Environment," Chis reiterates this message: This movement needs an extreme image makeover. Marketing gurus tell me that all those depressing facts environmentalists throw into the ether might make us think, but they'll never get us to act...The trick is to replace the doom and gloom of environmentalism with positive, upbeat, motivating messages that request a specific action. (paras. 4 & 8) For his part, Professor of psychology at St. Thomas University in Fredericton, New Brunswick, Doug McKenzie-Mohr, seeks to address these shortcomings with his take on social marketing – community-based social marketing (CBSM). Adapting his understanding of social psychology and human behaviour, McKenzie-Mohr "systematically looks at desired behaviours, actual behaviours, and the reasons behind any dissonance" (p. 178). By identifying and removing barriers to compliance, educating the population under consideration, and asking for personal commitment to participate, new norms are established, norms from which individuals no longer feel comfortable straying. Taking advantage of the fact, Mackenzie-Mohr and his convert Ken Donnelly, Solid Waste Manager in Durham County, get 90 percent buy-in to municipal recycling and composting programs (p. 179). As Chris mentions "Peer pressure is a powerful thing, even among adults. No one wants to be the nail that sticks up. That is what makes CBSM a hopeful tool" (p. 182). By acknowledging and working with what is known from social psychology, CBSM holds great promise for more sustainable behaviour change. In addition, CBSM, and social psychology at its root, realize that if you can get small behavior changes in place, people "become more susceptible to bigger changes," the foot-in-the-door technique of marketing. Says Chris of this phenomenon: "Ask people to stop idling their engines unnecessarily, then ask them to keep their tires fully inflated for fuel efficiency, then to slow down to conserve fuel, then to carpool, then to take a bus or ride a bike" (p. 182). Because such new behaviours may at first result in cognitive dissonance, "a feeling of discomfort caused by the realization that one's behaviour is inconsistent with one's attitudes or that one holds two conflicting attitudes," (Aronson, 2013, p. 174) people are likely to reduce this discomfort by convincing themselves that they must be the kind of person who recycles, conserves fuel, and so on until they find themselves convinced that they are indeed the kind of person who cares deeply about the environment and climate change.Continued on Next Page » Suggested Reading from Inquiries Journal
Inquiries Journal provides undergraduate and graduate students around the world a platform for the wide dissemination of academic work over a range of core disciplines. Representing the work of students from hundreds of institutions around the globe, Inquiries Journal's large database of academic articles is completely free. Learn more | Blog | Submit Latest in Book Reviews |